How do college students feel after a month of online classes?
Affected by the COVID-19 epidemic, colleges and universities all over the country started online teaching on the original starting date (around February 17th). As of March 14th, online teaching in most colleges and universities has been going on for about four weeks, and the online teaching has entered a relatively stable state. At this time, it is urgent to investigate and study the effect of online teaching in colleges and universities nationwide, so as to provide reference for college teachers to improve the effect of online teaching. Therefore, the research group of Hebei University conducted a survey on the effect of online teaching during the epidemic period for college students nationwide from March 14th to March 17th, 2020.
A total of 5094 valid samples were obtained in this survey. The respondents came from 113 universities in China, covering 13 disciplines, from the first year of university to the third year of graduate students, of which 34.9% were men and 65.1% were women.
According to the survey data, 69.16% of the students spend more than 4 hours in online teaching every day, among which 21.83% have more than 6 hours in online courses every day, and only 30.84% have less than 4 hours in online courses every day. It can be seen that the online learning task of college students is heavier.

First, the overall evaluation of online teaching-"It is not easy to say that I love you!"
Then, compared with the traditional classroom, what is the overall evaluation of students on the simple online teaching?
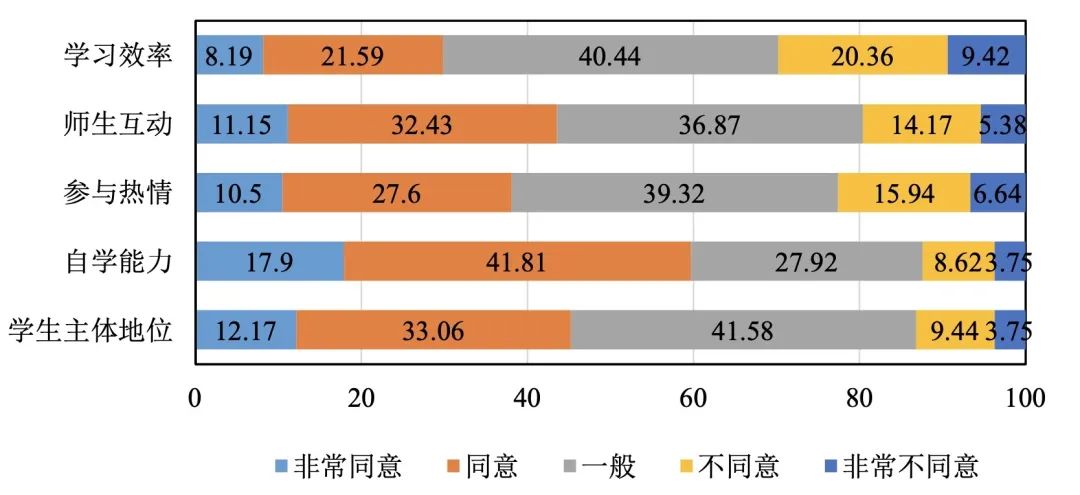
Figure 1 Percentage of overall evaluation of online teaching (unit:%)
1. Network teaching has no obvious effect on highlighting students’ dominant position.
Compared with traditional classroom teaching, online teaching highlights students’ dominant position. Do you agree with this statement? In the answer to this question, 45.23% of the students said "agree or strongly agree", 41.58% said "average" and 13.19% said "disagree or strongly disagree".
2. Online teaching has improved students’ self-study ability.
Compared with traditional classroom teaching, online learning has enhanced my self-study ability. Do you agree with this statement? According to the statistics of the answer to this question, 59.71% of the students chose "agree or strongly agree".

3. Web-based teaching has not well mobilized the enthusiasm of college students for class participation.
Compared with traditional classroom teaching, students are more enthusiastic about participating in online classroom. Do you agree with this statement? According to the statistics of the answer to this question, only 38.10% of college students said "agree or strongly agree" and as many as 22.58% said "disagree or strongly disagree".
4. The effect of online teaching in improving the interaction between teachers and students is average.
Compared with traditional classroom teaching, there is more interaction between teachers and students in online teaching. Do you agree with this statement? According to the statistics of the answer to this question, only 34.58% of college students said "agree or strongly agree" and as many as 19.55% said "disagree or strongly disagree".
5. The learning efficiency of students in online classroom teaching mode is not as good as that in traditional classroom.
Compared with traditional classroom teaching, online learning improves learning efficiency. Do you agree with this statement? According to the survey of this issue, as many as 29.78% of the students said "disagree or disagree very much", and only 29.78% said "agree or disagree very much".
Second, the choice of teaching methods after the epidemic-"still reluctant to part with you!"

Fig. 2 The situation of students’ choice of teaching methods after the epidemic.
The data shows that the teaching method of "traditional classroom teaching is the main method, supplemented by network teaching" has become the first choice for college students after the epidemic. This shows that the position of traditional classroom teaching cannot be replaced, but simple traditional classroom teaching and simple network teaching are not the first choice of students. On the contrary, the teaching method of "traditional classroom teaching is the main one, supplemented by network teaching" has become the first choice of college students. This requires that colleges and universities in China should seize the opportunity of implementing large-scale network teaching brought by the epidemic and vigorously develop network teaching in conjunction with traditional classroom teaching methods in the reform of teaching methods after the epidemic.
Third, the evaluation and analysis of the teaching effect of specific courses-"Old wine in new bottles, both are important"
We ask students to choose the specific course that they think is the best or the worst this semester to evaluate and answer the specific situation of this course.
1. Students have a high evaluation of the selected courses.
Among the scores of the selected courses, 74.07% students scored above 80, 18.59% students scored 60-80, and only 7.34% students scored below 60. It can be seen that students have a high evaluation of the effect of the selected courses.
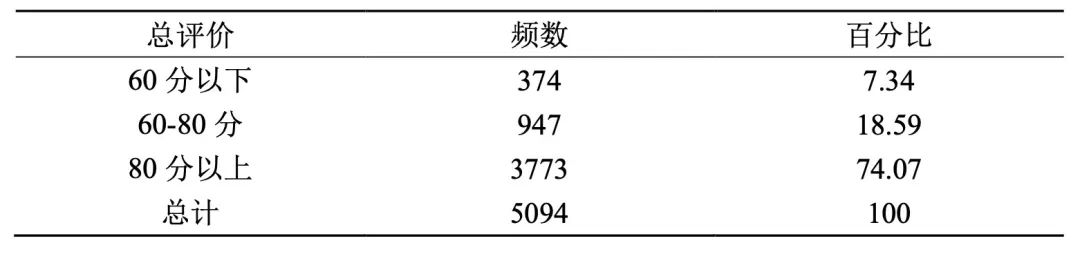
Table 1 Distribution of College Students’ Evaluation of Specific Courses

2. The teaching effect of specialized courses is better than that of public courses, the teaching effect is better in the morning, and the network teaching effect of small-scale classes is better.
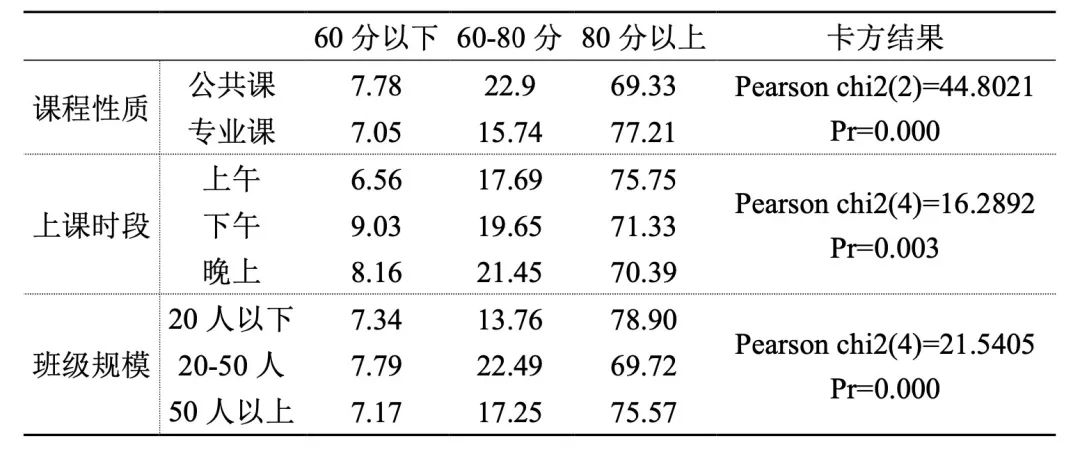
Table 2 Percentage of grading categories with different course nature, class time and class size (unit:%)
The results of data analysis show that there are significant differences in the teaching effect of different courses, different class periods and different class sizes. The teaching effect of specialized courses is better than that of public courses, the teaching effect of morning classes is better, and the network teaching effect of small-scale classes is better.
3. The teaching effect of live video is obviously better than other methods.
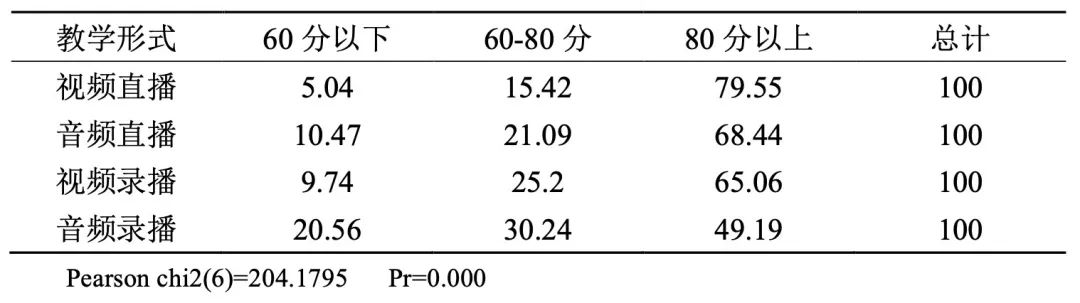
Table 3 Percentage distribution of teaching effect scoring categories by teaching form (unit:%)
The data shows that the teaching effect of live video is better than other forms, which also shows that "seeing is believing". Although students study at home, they are still eager for "face-to-face" real-time classroom form.
4. Courses with better image and sound transmission effect have better teaching effect.
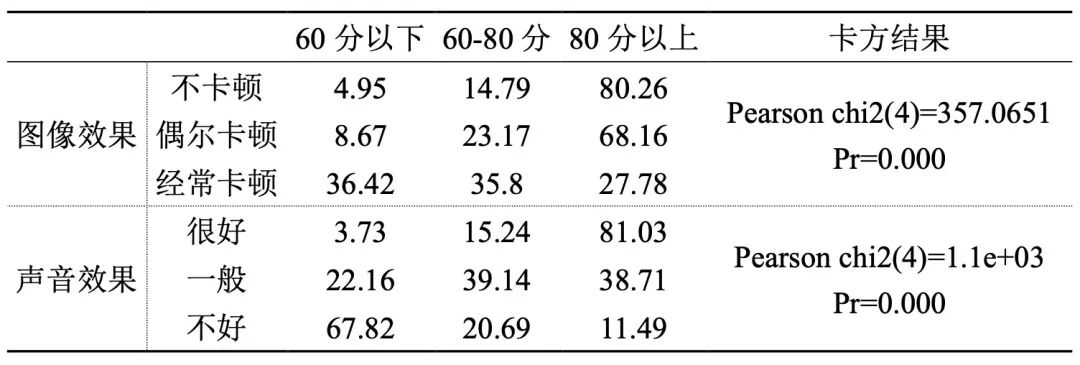
Table 4 Percentage of course scores with different image effects and sound effects (unit:%)
The biggest feature of network teaching is that it is subject to the network transmission situation. The results in Table 4 show that different network conditions and sound transmission effects will bring different teaching effects, and the evaluation of teaching effects with good network conditions and sound transmission conditions is also better.

5. Electronic textbooks and supplementary materials are provided, and the teaching effect is better.
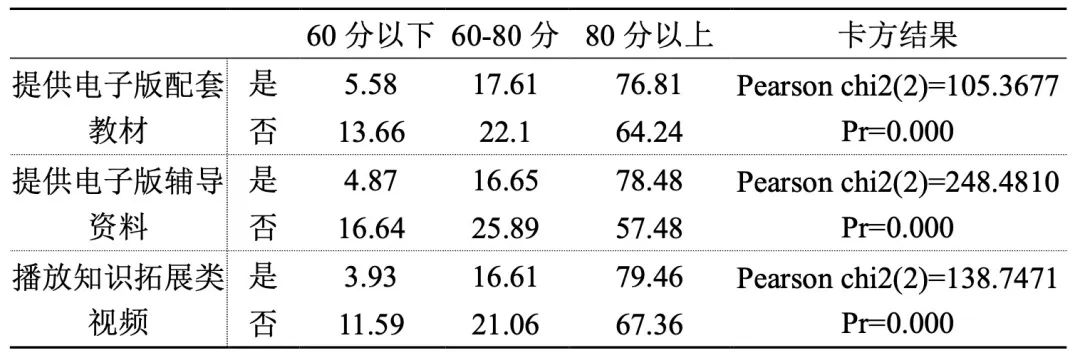
Table 5 The provision of all kinds of course resources and the scoring group of course teaching effect
During the epidemic period, students can’t go to school to get paper-based course materials such as textbooks and teaching AIDS, so whether online courses provide rich electronic course resources has become one of the factors that affect the teaching effect.
6. Online check-in and preview tasks are arranged in advance, and the online teaching effect is better.
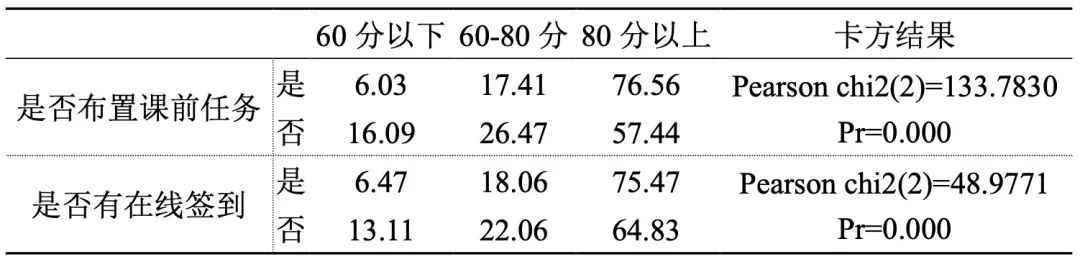
Table 6 Pre-class process and course teaching effect score grouping
The results in Table 6 show that the pre-class task arrangement and electronic sign-in of online courses are also factors that affect the teaching effect of the course.

7. The course of using electronic blackboard books has a good teaching effect.
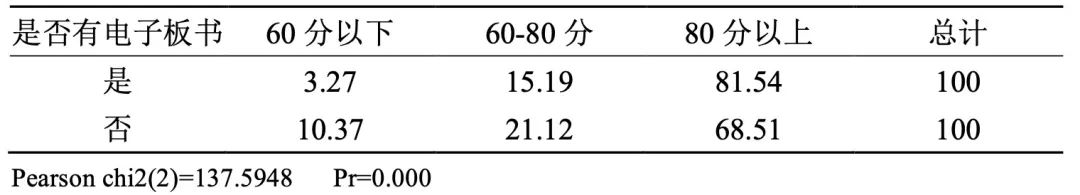
Table 7 Percentage distribution of teaching effect scoring categories by whether there are electronic blackboard books (unit:%)
Although the fluency and effect of online teaching electronic blackboard can’t be compared with the physical blackboard, the data show that the teaching effect of the course using electronic blackboard in the course is obviously better.
8. The higher the number of teacher-student interactions and the number of students who speak, the better the classroom effect.
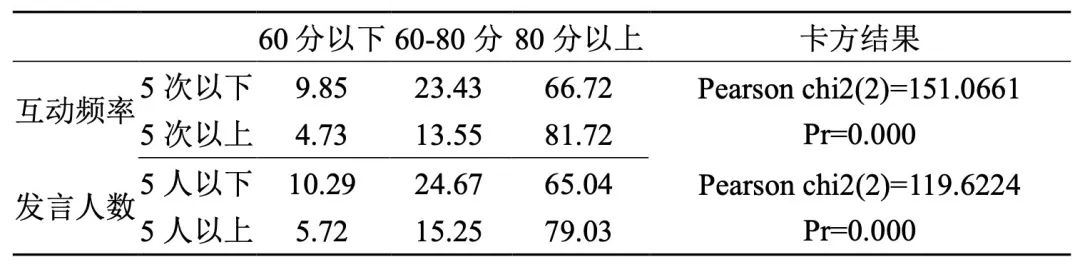
Table 8 Teaching effect evaluation groups of courses with different times of teacher-student interaction and number of students who speak (unit:%)
Classroom interaction is an important link and means to improve students’ participation and enthusiasm in class, which is also fully applicable to online teaching.
9. The course of homework and answering questions in time after class is arranged, and the teaching effect is good.
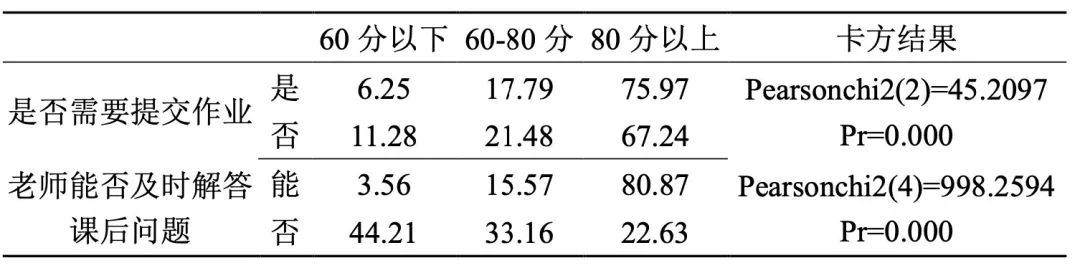
Table 9 After-class links and teaching effects
Paying attention to after-class links can effectively improve the teaching effect of the course, which is also fully applicable to online teaching.
10. Courses that can be played back have better teaching effect.
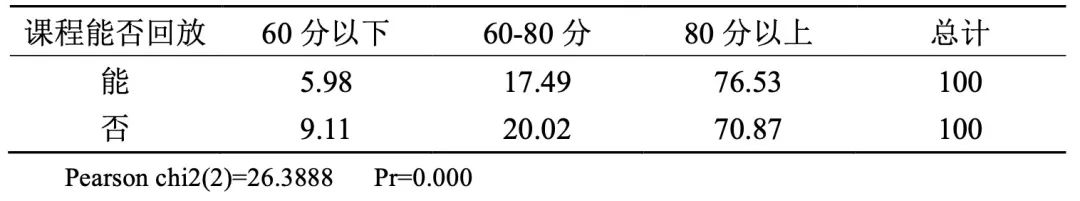
Table 10 Percentage distribution of teaching effect scoring categories by whether courses can be replayed (unit:%)
Online courses can be recorded and replayed conditionally, and the teaching effect of courses with replay is better, which requires teachers to make full use of the advantages and specialties of online teaching.
To sum up, the factors that affect the teaching effect of online courses are not only the traditional teaching factors such as preparation of teaching resources before class, interaction in class, homework and counseling and answering questions after class, but also the specific class form and the transmission effect of images and sounds. That is to say, online teaching only changes the teaching way and carrier, and its connotation has not changed except choosing the appropriate class form and smooth network guarantee, which depends on the energy input of teachers in the teaching of this course. It is called "new bottles and old bottles"

Thanks: The epidemic is dissipating, and spring is just around the corner. Thanks to the students from all corners of the country, and thank you for your sincere answers. Once again, I wish every one of you.
Member of research group
Wangpenggang
Associate Professor, Institute of Population Studies, School of Economics, Hebei University
Jia zhike
Associate Professor, School of Philosophy and Sociology, Hebei University
Wang Li
Master student in Population Institute of School of Economics, Hebei University.
Hao Hongfei
Master student in Population Institute of School of Economics, Hebei University.
This survey was funded by the 2019 Hebei Higher Education Teaching Reform Research and Practice Project "Teaching and Reform Research on Social Investigation Research Methods with Literacy Cultivation as the Goal".
Editor in charge: Associate Professor, School of Social and Population Studies, Renmin University of China, Li Ting.
Editor of this issue: Master candidate of School of Social and Population Studies, Renmin University of China.
The manuscript was first published in WeChat official account, the WeChat of Serious Demography Gossip. Please indicate the source, author’s name and "from The Paper Paike Channel" for reprinting. Please contact yansurenkou8gua@163.com for reprinting and cooperation.